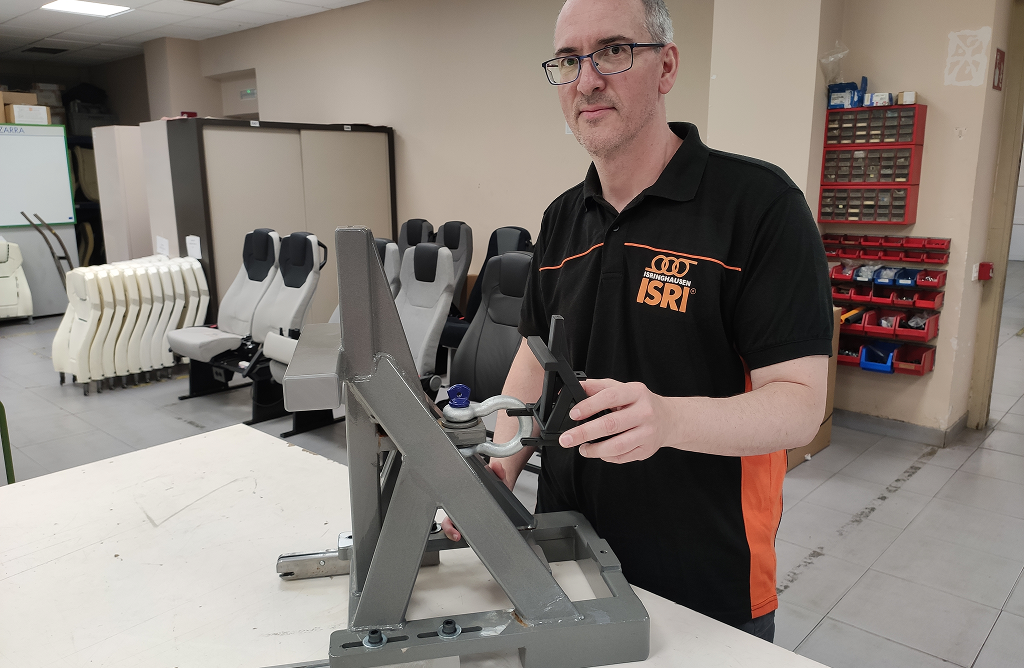
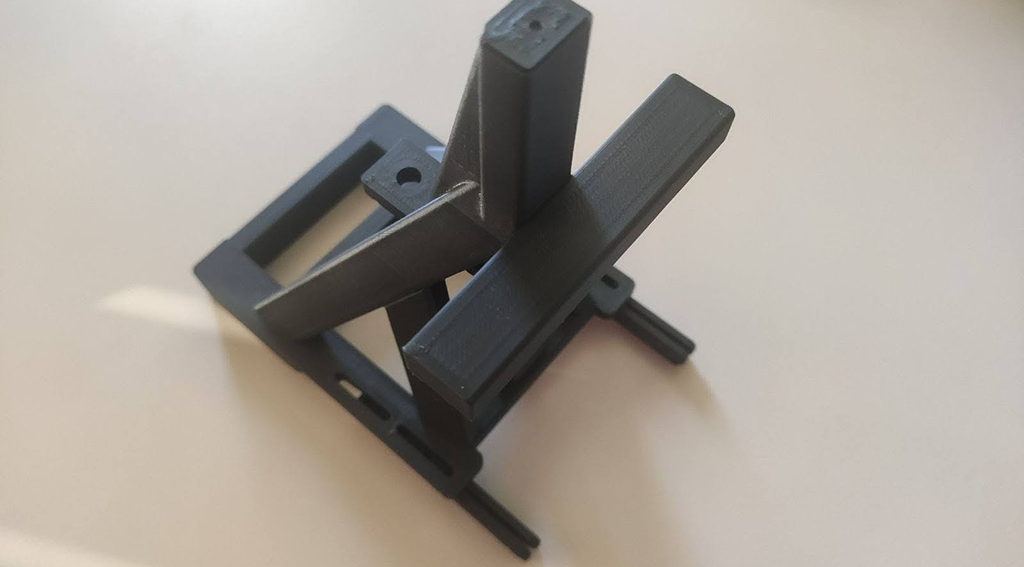
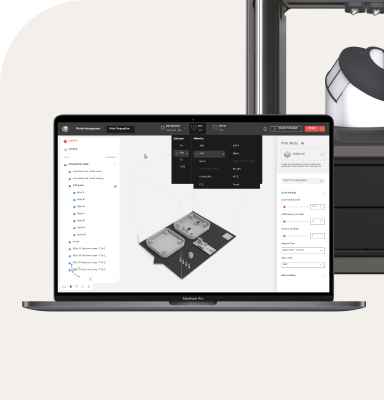
This 3D printed side cover is part of a new seat model currently in the industrialisation phase, intended for use in seating applications. Made from Winkle's Jet Black PLA, the part features a matte finish and was produced on the UltiMaker S6 3D printer. It serves as a functional prototype for aesthetic and fit testing.
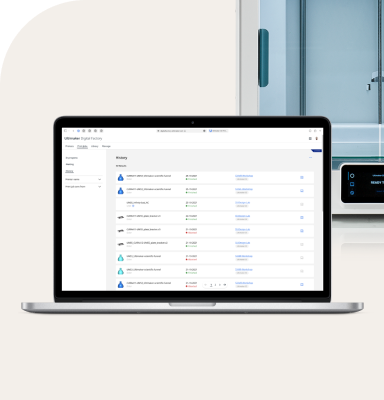
Typically, Alberto receives ready-to-print 3D files from the Isringhausen R&D department, although he occasionally creates designs himself. By leveraging UltiMaker Cura, Alberto can slice the models before sending them to print.
For printing prototypes, Alberto uses PLA, PVA, and flexible TPU. For end-use parts exposed to high temperatures, such as components used in vehicles like a bus seat bracket, he switches to PET CF to ensure durability and heat resistance.
UltiMaker is a professional brand, designed specifically for use in factories and demanding industrial workflows - that’s exactly what we are looking for.
Looking to speed up prototyping? Get speed and precision with the UltiMaker S6
With UltiMaker S6 is your easy access to faster prototyping and new innovations. Backed by Cura Cloud, UltiMaker Digital Factory and hundreds of validated materials, the S6 is the easiest gateway into the full UltiMaker ecosystem, delivering first-class productivity without compromising the rock-solid reliability your workflow demands.
If you want to know more about how 3D printing could solve your prototyping challenges, talk to our experts.