In part one and part two of our series on 3D printing materials, we have taken a look at a wide variety of material-related topics, from the FFF process itself to specific use cases and mechanical properties. In the third and final installment, we will cover all things filament, from the additives and blends that give materials mechanical properties to an overview of filament production.
What is 3D printing filament?
From the first part of our 3D printing materials series, we know that FFF 3D printing uses thermoplastic – a plastic polymer that becomes pliable and moldable when heated, and a solid when cooled.
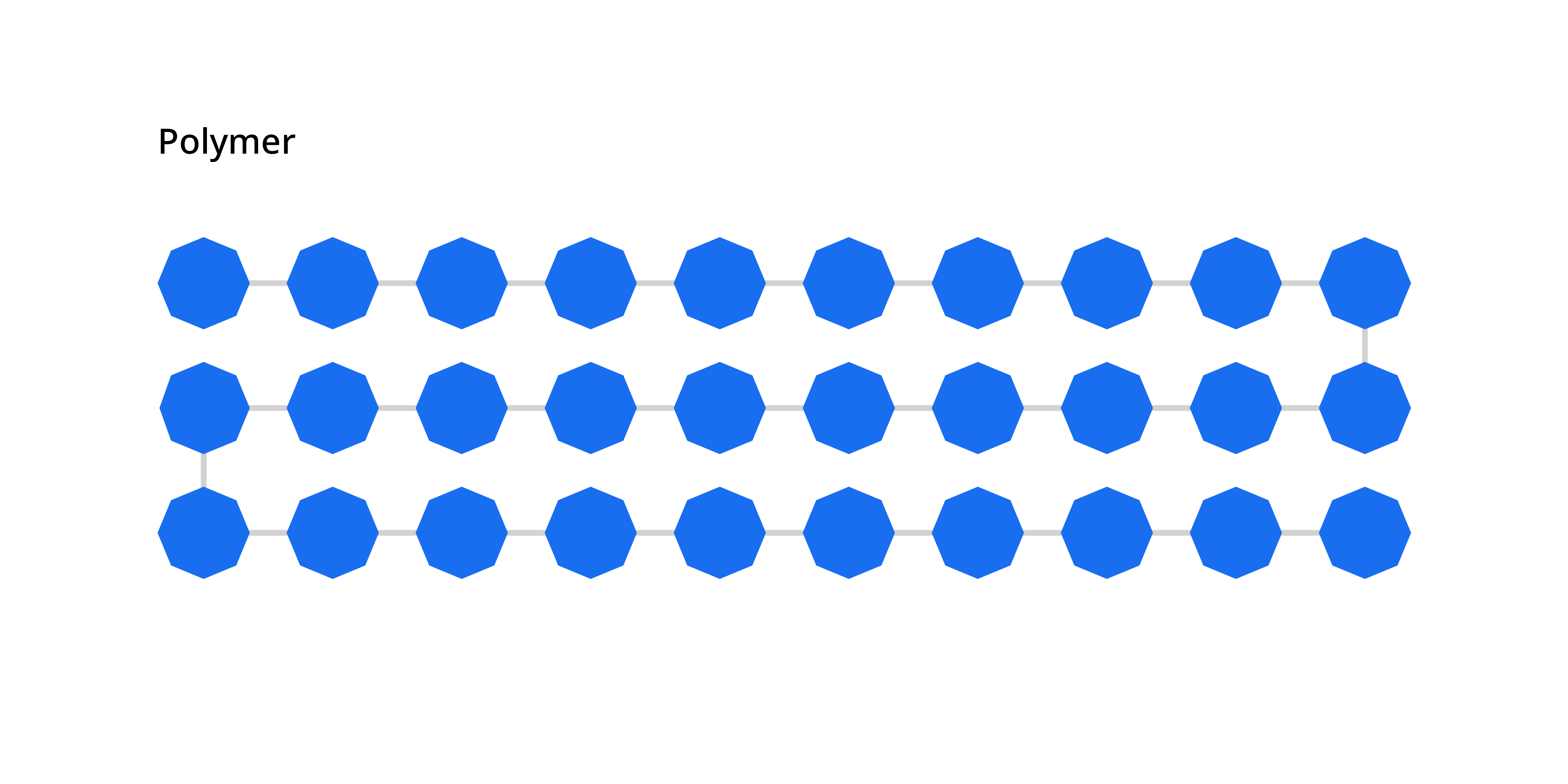
A polymer (“poly” meaning “many”) is a substance that consists of multiple molecules called monomers (“mono” meaning “one) that are able to bond in long chains in a process known as “polymerization.” Chains of repeating monomers give polymers unique properties such as flexibility or rigidity.
An illustration of a monomer
An illustration of a polymer
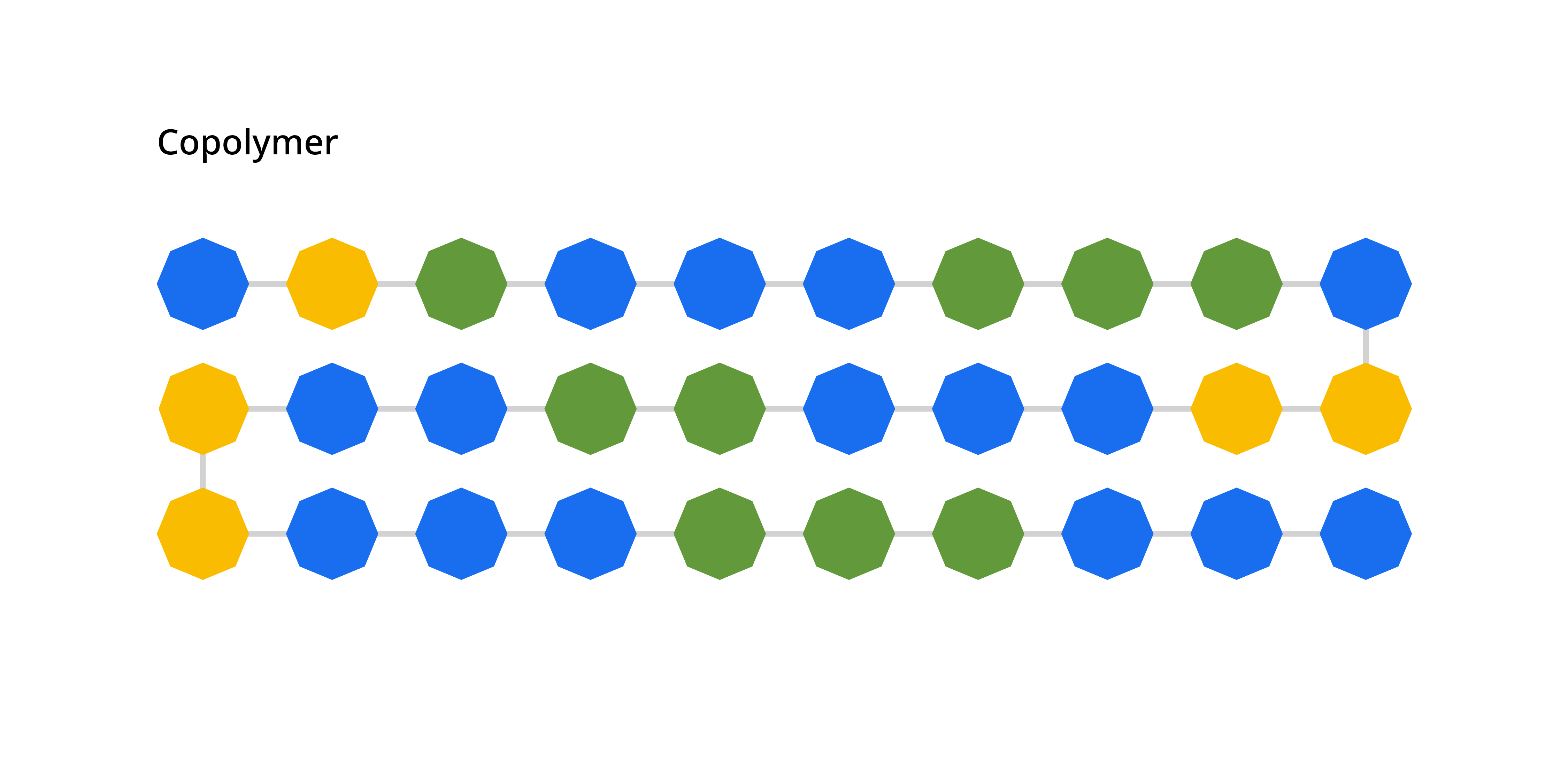
A copolymer, on the other hand, is a substance consisting of multiple monomers of differing type bonded together. In FFF 3D printing, copolymers can offer different mechanical properties needed for specific applications and use cases.
An illustration of a copolymer
How filament is made
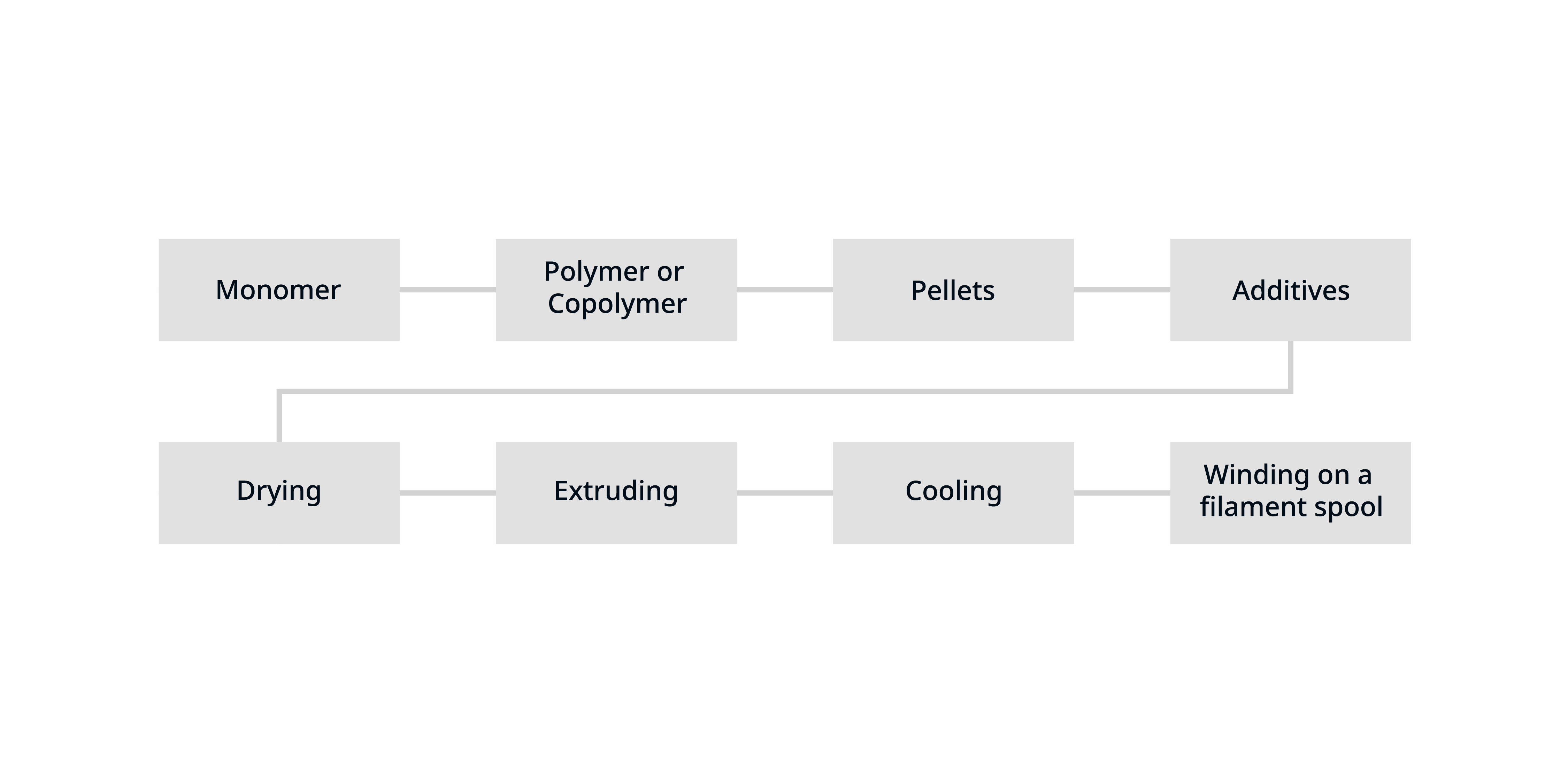
The process of creating 3D printing filament is called "compounding." First, raw plastic resin in the form of pellets is produced. These pellets can be mixed with additives to obtain desired mechanical properties. The mixture is then dried, extruded to the desired width (usually 1.75 or 2.85 mm), and wound on a spool. Once wound, the material is ready to be used in 3D printing.
The filament production process
Additives and blends
As we know, additives are added to plastic resin to obtain specific mechanical properties. Fillers, including glass or carbon fibers, can make filament stronger and heavier. Pigments add color. Antioxidants can be used to create filaments with UV and chemical resistance. Antistatic agents offer electro-static discharge (ESD) protection. Additives can also be used to reduce impact resistance, create flame-retardant properties, or increase flexibility.
Blends, meanwhile, are created when two or more polymers are mixed together and used to create 3D printing filament. Pellets of polymers are combined at the beginning of the filament manufacturing process. Blends are used to combine the strengths of different polymers to create a filament that’s better suited for its applications.
Find the perfect material
With Ultimaker’s open material system and the Ultimaker Material Alliance, you can almost certainly find a filament that’s suited to your needs. And be sure to visit the Ultimaker Marketplace for an overview of all filaments from Ultimaker and our partners. There, you can download print profiles that will allow you to achieve the results you want, as quickly and easily as possible.