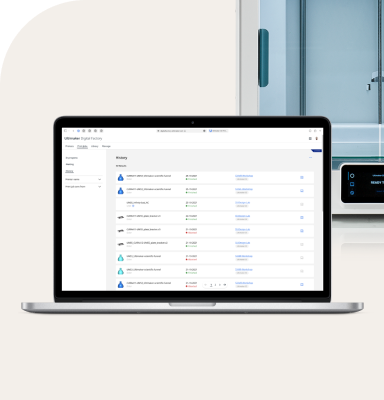
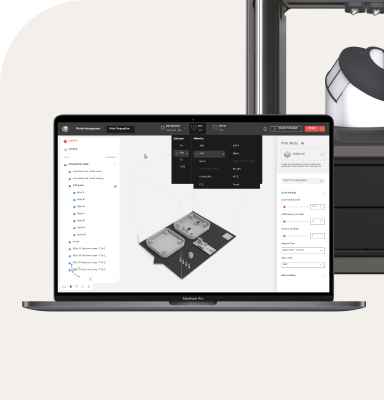
Improved agility and resilience in supply chains
Beyond individual benefits, distributed manufacturing significantly fortifies the overall supply chain, enhancing both its agility and resilience. This decentralized approach minimizes vulnerabilities and allows for quicker adaptation to unforeseen circumstances.
Distributed manufacturing offers significant benefits for improving supply chain agility and resilience. By decentralizing production across multiple locations, companies can create more flexible and adaptable supply networks that are better prepared to handle disruptions and fluctuations in demand.
Key benefits for supply chain agility and resilience include reduced dependency on single sources, faster response to local demand, shortened supply chains, improved inventory management, and enhanced risk mitigation. The geographic diversification helps companies navigate regional challenges such as natural disasters, political instability, or trade disputes.
The adaptability provided by distributed manufacturing enables companies to pivot quickly in response to supply chain disruptions. For instance, during the COVID-19 pandemic, businesses with distributed production capabilities were often able to continue operations by shifting production to unaffected areas.
Furthermore, distributed production models facilitate scalability. Companies can more easily adjust production up or down based on demand fluctuations in specific markets and tailor products to regional preferences.
Localized production and customization capabilities
One of the most compelling aspects of distributed manufacturing is its ability to foster localized production, opening doors to unprecedented customization possibilities. This capability allows companies to cater to niche markets and individual customer needs with remarkable precision.
Distributed manufacturing enables companies to produce goods closer to consumers, unlocking opportunities for localized production and customization. This decentralized approach offers several key benefits:
Enhanced customization: Local manufacturing facilities can more easily tailor products to regional preferences and requirements, allowing for greater product personalization and market-specific offerings.
Faster response to market demands: Proximity to customers enables quicker adjustments to changing local needs and trends. Companies can rapidly iterate designs and produce small batches to assess market response.
Reduced lead times: By producing goods closer to the point of demand, distributed manufacturing significantly reduces delivery times, improving customer satisfaction.
Leveraging local expertise: Decentralized production allows companies to tap into regional manufacturing knowledge and skills, which can lead to innovative adaptations of products for specific markets.
Mass customization at scale: Technologies enable cost-effective production of customized goods in smaller quantities, making mass customization economically practical.
The localization capabilities of decentralized manufacturing extend beyond production. Companies can also source materials locally, collaborate with local designers and engineers, adapt packaging and marketing materials to suit local preferences, and offer personalized services such as on-demand spare parts or product modifications.
Sustainability and waste reduction in manufacturing
In an era of increasing environmental consciousness, distributed manufacturing offers a pathway to more sustainable practices and significant waste reduction within the manufacturing sector. By minimizing transportation and optimizing resource use, this model aligns with the goals of a circular economy.
Distributed manufacturing offers sustainability benefits and waste reduction advantages compared to traditional centralized production models. By localizing production nearer to consumers, this approach can substantially decrease the environmental impact of manufacturing.
Key sustainability benefits include reduced transportation emissions, decreased inventory waste, optimized resource utilization, and enhanced recycling potential. Producing goods closer to their point of use dramatically cuts shipping distances and associated carbon emissions from freight transport.
Distributed manufacturing also enables more sustainable practices through localized material sourcing, energy efficiency, and reduced packaging waste. Smaller production facilities often incorporate more energy-efficient technologies and can more easily integrate renewable energy sources.
The waste reduction potential is noteworthy. FDM 3D printing technologies can produce parts with minimal material waste compared to traditional methods. Production that matches demand eliminates overproduction. Additionally, local production of spare parts can extend the life of products, reducing replacements and waste.